- MovieMate Developer Guide
MovieMate Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to Akshay, Ngiap Hin, and AddressBook3 for the help.
Setting Up
Setup guide for developing MovieMate can be found here.
Design
Architecture
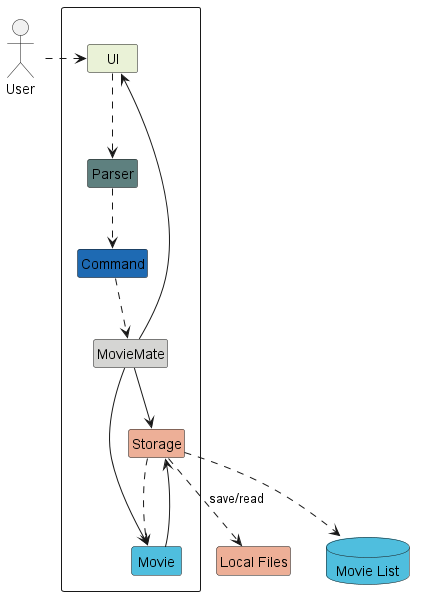
The Architecture Diagram above gives a high-level design of MovieMate.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main Components
The main class is MovieMate. It is responsible for managing
calls to the other classes and establishing required files.
MovieMate makes use of some core general components: (LINKS TODO)
-
UI: The UI of the app. -
Storage: Responsible for read/write of data. -
Parser: Interprets user input and read data. -
Command: Logic of MovieMate.
Finally, all the movie-related classes are packaged in Movie. Among its contents are MovieList and Movie.
Interactions
Please refer to the example sequence diagram below to show how components interact with each other.
For instance, we have a scenario where the user inputs watched La La.
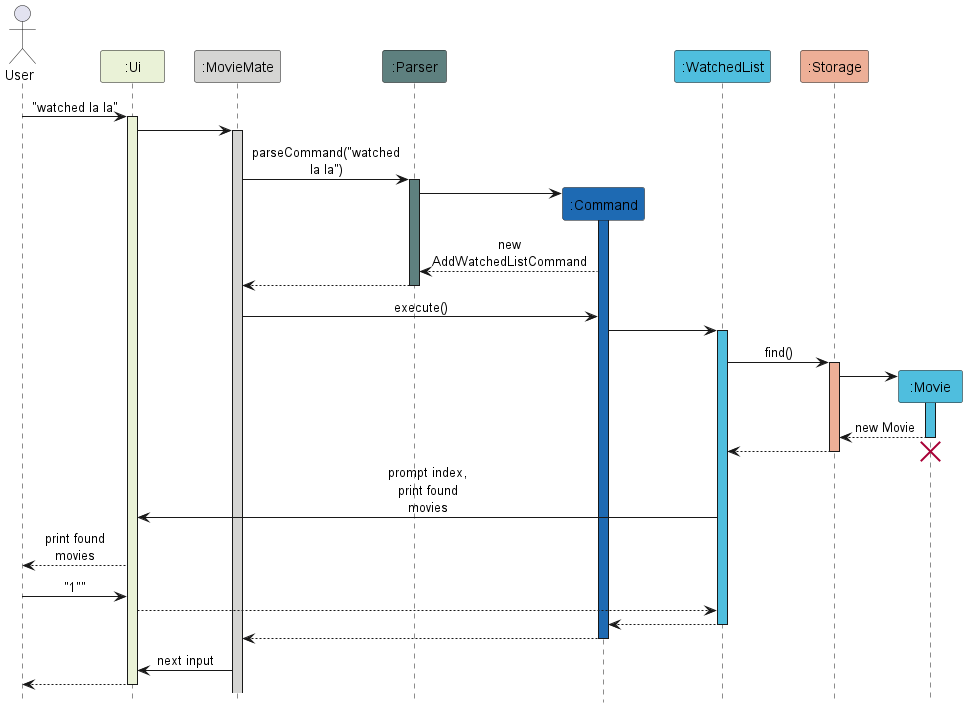
As you can see, individual components handle specific responsibilities, but all mostly controlled by MovieMate.
The below sections go into detail on each component.
UI Component
Package here.
Because MovieMate is purely a command-line interface, the UI component is very simple. It handles input and output.
UI only helps to receive input. Further input validation and parsing is handled by Parser.
UI is the main driver for printing feedback to the user. All the pre-written messages are stored in UI. Thus, just about every component has an association with UI, going through UI to connect to the user instead of directly addressing the user.
Parser Component
Package here.
Parser is utilised by UI to make sense of user input. One of its main methods is parseCommand, which returns a Command
based on the input. Parser thus relies on Command.
Parser also has another method to parse index, which makes use of Integer::parseInt
but adds functionality to check for index bounds. This method is heavily used by features related to our Movie lists.
Storage Component
Package here.
The Storage
class mainly deals with reading and writing of user data for persistence.
To note, the Storage::writeToFile method is called when the user issues an exit command.
Exiting in other ways (such as closing the window) may lead to unsaved data.
Note that Storage itself does not technically depend on other classes like MovieList. Its methods are built to be general-purpose
as much as possible so other classes may potentially use it in the future for similar purposes.
The MovieDatabase
and ReadCSVFile
classes are also included in this package. These deal with methods to read, store, and parse through the list of movies.
For a more detailed look at the list of movies, please see the Setup Guide).
Upon opening of MovieMate, MovieDatabase stores the movies in its collection (In the form of Movie class). This allows
for easy parsing of data.
Command Component
Package here.
Command
is an interface that specifies a single abstract method, execute. Each Command performs a task in MovieMate.
Commands are issued by the user, which are parsed by Parser into Command instances to be executed by MovieMate.
Most Commands interact with classes within the Movie package. Some are utility Commands (such as ExitCommand or HelpCommand)
For a full list of command functionalities, you may refer to the User Guide. Also see Implementation on how some Commands are built.
Movie Component
Package here.
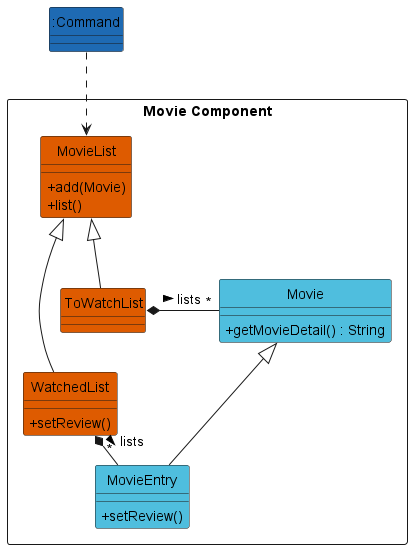
This component deals with the movies, which are a core data point in MovieMate. This includes Movie classes themselves
and MovieList classes that form a collection of Movies.
Both Movie Lists do not differ by much, but the Watched list tracks movies you have watched, and thus has extra capabilities,
that is, assigning reviews. The MovieEntry class extends off Movie to add a Review component (See Review).
Implementation
Review Feature
API: Review.java
Here’s a partial class diagram of the Review component:
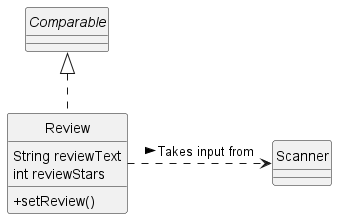
The Review component contains both a descriptive review reviewText,
and a numerical review reviewStars (0 to 5 inclusive). Both are modified through the
setReview() method.
Review implements Comparable, and is compared
through simply comparing reviewStars.
How the Review component works:
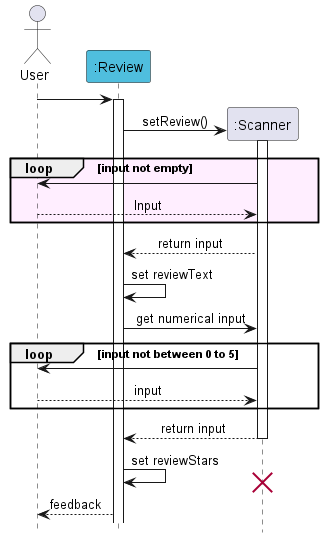
Step 1. setReview() is called, which creates a Scanner
to read user input.
Step 2. User input is read (multiple lines) until a blank line is found.
Then, reviewText is updated with the text input.
Step 3. Next, user is prompted for a numerical input (with input validation).
This value is updated into reviewStars.
Step 4. Finally, Scanner is closed and Review is done setting.
Movie List Feature
API: Movie.java
Here’s a partial class diagram of the MovieList component:
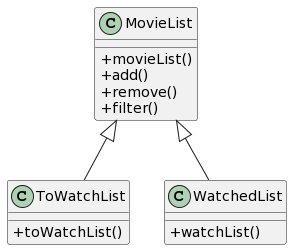
The MovieList component has two inherited classes ToWatchList and WatchedList. It contains a public method movieList for creating an empty movie list,
which also has a overloaded constructor for creating a movie list with an existing list.
In addition, MovieList contains a public method add, which will search for relevant movies in the database
and help user to add a new movie to the movie list. It also contains a public method filter,
which will filter the movies with certain genre and display it to the user. The public method remove, will remove a movie from the list,
and this will be implemented soon. Other methods such as getMovie() and toString() are also included in MovieList.
How the MovieList.add(String inputTitle) component works:
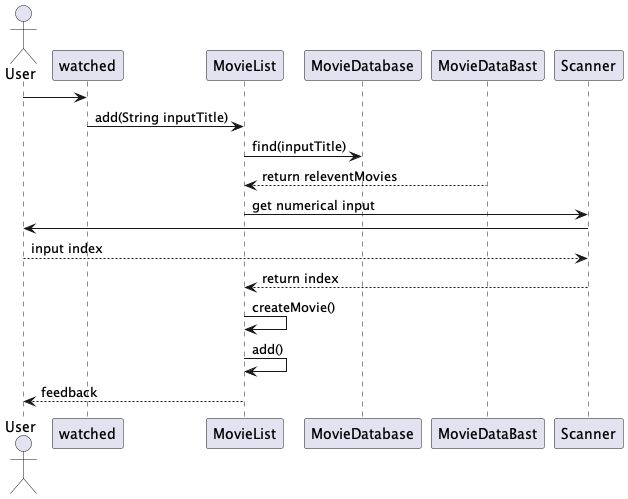
Step 1. add(String inputTitle) is called, which continues to call find() in MovieDatabase to search for the relevant movies.
It will then display at most five movies that matches the inputTitle.
Step 2. Next, user is prompted for a numerical input (with input validation). This value indicates the movie index chosen by the user from the list.
Step 3. Next, createMovie is called to create a new Movie object according to the index and add the movie to the movie list.
Step 4. The add(String inputTitle) will show feedback message to the user.
Step 5. The add(String inputTitle) has finished everything and returned.
How the MovieList.remove() component works:
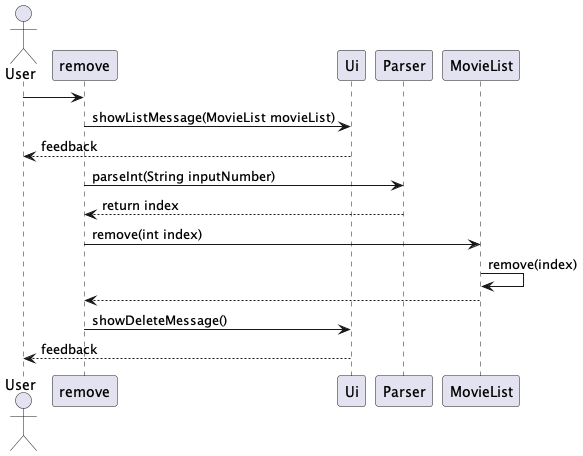
Step 1. remove command is entered, which continues to call showListMessage() in Ui to
show the user the movies in the list.
It will then display all movies from watched list or to-watch list, allowing the user to easily pick the movie for deletion.
Step 2. Next, user is prompted for a numerical input (with input validation). This value indicates the movie index chosen by the user from the list.
Step 3. Next, remove() is called to remove a Movie object according to the index and delete the movie to the movie list.
Step 4. The function will call showDeleteMessage from Ui, which will show feedback message to the user.
Step 5. The remove command has finished everything and ended.
How the MovieList seedetail component works:
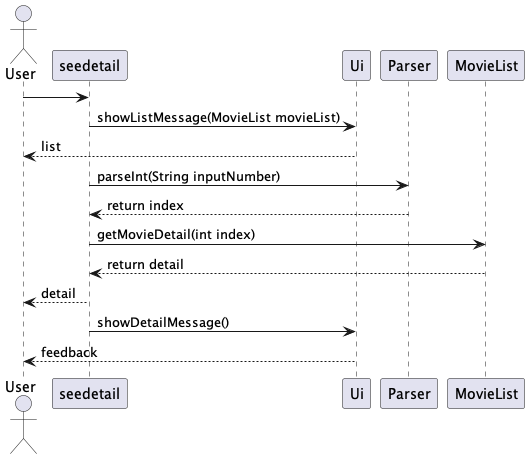
Step 1. seedetail command is entered, which continues to call showListMessage() in Ui to
show the user the movies in the list.
It will then display all movies from watched list or to-watch list,
allowing the user to easily pick the movie for viewing detail.
Step 2. Next, user is prompted for a numerical input (with input validation). This value indicates the movie index chosen by the user from the list.
Step 3. Next, getMovieDetail() is called to get the detail of a Movie object
according to the index and return the detail of the specified movie.
Step 4. The function will call showDetailMessage from Ui, which will show feedback message to the user.
Step 5. The seedetail command has finished everything and ended.
How the MovieList.filter(String genre) component works:
Step 1. filter(String genre) is called. getClass() and getName() are then called to get the relevant list’s class and name.
For example, if filter is done on the WatchedList, “In WatchedList:” is displayed.
Step 2. An integer i is initialized with a value of 1.
Step 3. Iterate through the MovieList. For each movie, getGenres() is called to obtain its array of genres, which is checked
to see if it contains the input genre. If true, a description of the movie will be displayed on a new line and i is
incremented. If false, nothing will be displayed.
Step 5. After the entire iteration is complete, if i == 1, it means no movies were found containing the input genre in their
genre array. Feedback message displayed accordingly and filter returns.
Product scope
Target user profile
This product is for moviegoers who would prefer a simple way to book movies and keep track of, and rate what they have watched.
Value proposition
MovieMate provides a platform for the avid moviegoer to keep track of the movies they’ve watched, rate the movie that they just watched, or keep track of what they plan to watch.
User Stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I can … |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0 | new user | see usage instructions | refer to them when I forget how to use the application |
| v1.0 | user | list a watched/ to-watch movie list | see all movies in my watched/ to-watch list |
| v1.0 | user | add a watched/ to-watch movie by short name | add a watched/to-watch movie without having to type out the whole name |
| v1.0 | user | add a watched/ to-watch movie | keep track of the movie I have watched/ want to watch |
| v1.0 | user | delete a watched/ to-watch movie | keep track of the movie I have watched/ want to watch |
| v1.0 | user | store my movie lists on my laptop | easily find the information of my movie list |
| v1.0 | user | exit the program smoothly | continue to work on other things. |
| v2.0 | user | add a review to my watched movie | keep track of my opinion about the movie |
| v2.0 | user | delete a review to my watched movie | keep track of my opinion about the movie |
| v2.0 | user | see detail of a movie | know whether I have watched the movie or I would like to watch it |
| v2.0 | user | get some random movie of certain genre | get some inspiration of which movie to watch |
| v2.0 | user | make sure there is no duplicate in my watched list and to-watch list | prevent from watching the movie I have watched before |
| v2.0 | user | get proper feedback message for the command entered/ executed | know whether the command was executed successfully |
Non-Functional Requirements
- Efficiency: The application should be able to respond to user requests quickly, even for large movie lists.
- Reliability: The application should be able to store and retrieve movie lists accurately and consistently.
- Security: The application should protect user data by securely storing movie lists.
- User-friendly interface: The application should have a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and understand.
- Compatibility: The application should be compatible with different operating systems and devices.
Glossary:
- Movie: A film that a user wants to watch or has watched.
- Watched list: A list that contains the movies the user has already watched.
- To-watch list: A list that contains the movies the user wants to watch.
- Review: The user’s opinion or feedback about a movie.
- Movie list: A collection of movies, either the watched list or to-watch list.
- Genre: A category of films that share similar themes, plots, and characters.
Instructions for manual testing
-
Download and Run jar file from releases. Download the latest jar release and copy it into a directory (preferably empty). Run in the commmand line
java -jar <jar_file_name>.jarwhere<jar_file_name>is the name of the jarfile downloaded. -
Run some commands as found in User Guide.